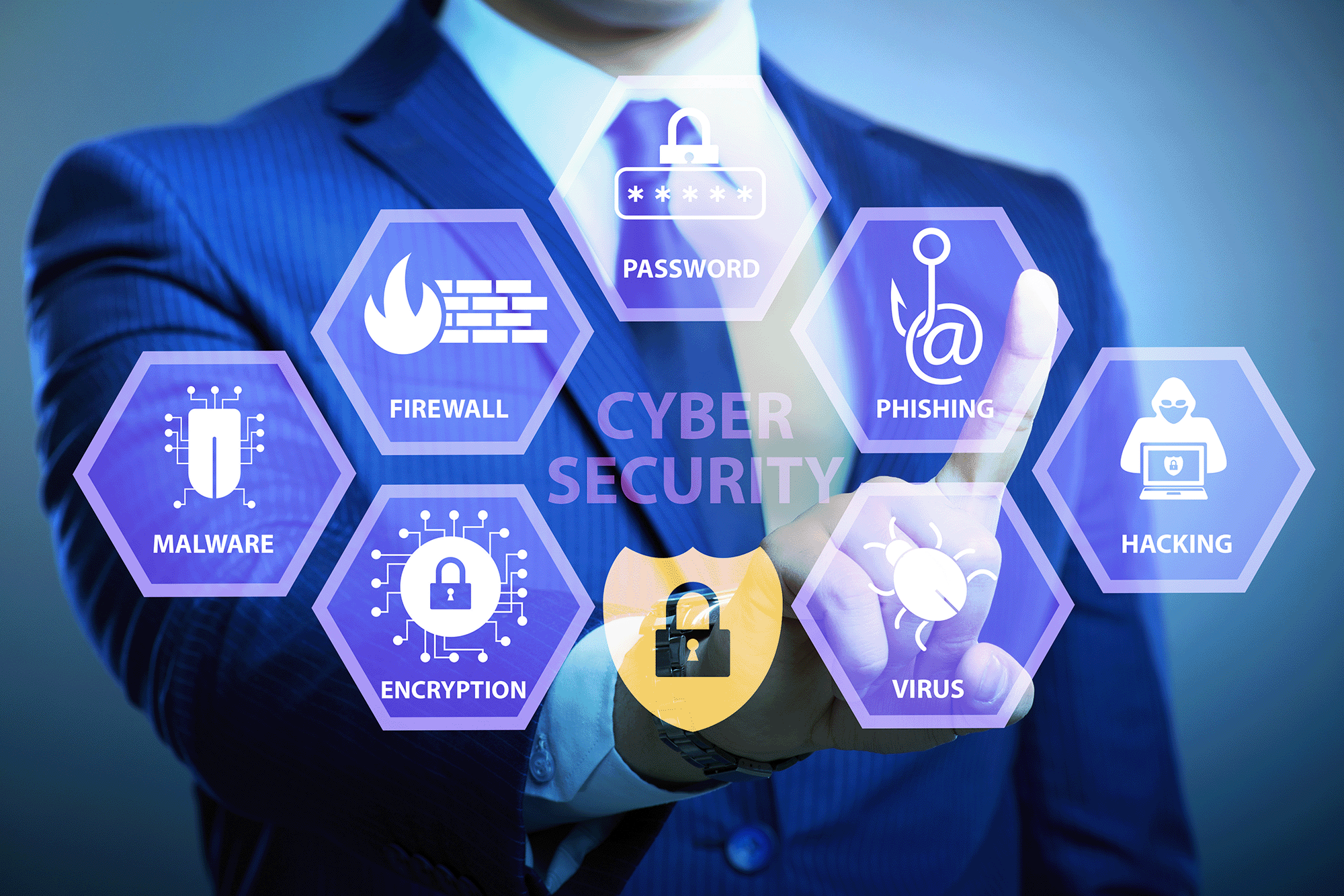
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an essential technology you can use to keep your cloud services and line of business applications secure and mitigate the risk of hacking-related breaches and data loss.
What is MFA?
MFA, also known as 2FA (two-factor authentication), ensures whatever application or service you are logging in to is double-checking that the request is coming from you by confirming the identity of a user before granting access.
This security step makes it more difficult for hackers to break into your systems and data. Even if they manage to get hold of a password, an attacker must have access to the device or account that is used for the second factor of authorisation in addition to the password.
How Does MFA Work?
Different 2FA methods use varying processes but rely on the same underlying workflow.
Typically, a 2FA transaction happens like this:
- The user logs in to the website or service with their username and password.
- An authentication server validates the password, and the user becomes eligible for the second factor if correct.
- The authentication server sends a unique code to the user’s second-factor device.
- The user confirms their identity by approving the additional authentication from their second-factor device.
- Both stages or proofs of identity must be passed to grant access to the service.
Five Reasons Why Your Business Should Use MFA
MFA is essential to cloud and web security because it immediately neutralises the risks associated with a password that might be hacked or guessed. Without approval at the second factor, a password alone is useless.
Compliance
In the first instance, MFA is one key factor that Cyber Insurance Policies require. In addition to Cyber Insurance, it may be needed to comply with other regulators such as those in the finance, health and Government industries. MFA also forms part of the ACSC’s ‘Essential Eight’ Strategies to Mitigate Cyber Security Incidents to progress an organisation’s maturity model and improve security posture.
Protect Against 3rd party Data Breaches and Weaker Passwords
MFA assists in protecting against 3rd party data breaches and weak passwords. Should a hacker steal a password or PIN, they would still need to obtain access to the other authentication method and token for your account.
Remote Access Protection
As organisations increasingly move to hybrid work environments where employees can work off-site to access company files, a business’ Citrix, Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and Virtual Private Network (VPN) must be paired with MFA.
Allowing remote access to files is essential for productivity. However, it does add an extra level of security vulnerability and increases an organisation’s attack surface. RDP access should be secured firstly via a VPN connection where MFA is enabled. This security measure should be allowed for all future connections to the Windows environment where the end-user is asked to verify their identity by MFA each time.
Improved Cyber Security Resiliency
Using MFA can help mitigate against the use of non-authorised/unmanaged devices, therefore enhancing your cyber security resiliency. Enabling MFA helps protect against unauthorised access to files from devices that are not secure or people who are not meant to have access.
Cyber resiliency refers to a business limiting the impact of security breaches via security processes and systems. MFA assists in strengthening a business’ cybersecurity posture, reducing the risk of data loss and, therefore, financial loss, business disruptions and other adverse impacts resulting from a security incident.
Single Sign-On for Applications
As a fundamental security strategy, your business’s MFA system must be user-friendly and secure. Applications with Single Sign-On (SSO) including Microsoft Office 365 provide users with a consistent login experience for all their applications. Consistency and ease of use are core considerations for businesses considering an MFA tool that provides SSO.
What next?
If your business needs to review or implement an MFA tool, contact our team.

 Canada
Canada LATAM
LATAM New Zealand
New Zealand UAE
UAE United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States